Meta-analytic functional decoding¶
Discrete decoding¶
Discrete decoding approaches characterize subsets of the Dataset or regions of interest, rather than continuous maps.
The BrainMap approach¶
nimare.decode.discrete.BrainMapDecoder(), nimare.decode.discrete.brainmap_decode()
The BrainMap method for discrete functional decoding performs both forward and reverse inference using an annotated coordinate-based database and a target sample of studies within that database. Unlike the Neurosynth approach, the BrainMap approach incorporates information about the number of foci associated with each study in the database.
Select studies in the database according to some criterion (e.g., having at least one peak in an ROI).
For each label, studies in the database can now be divided into four groups.
Label-positive and selected –>
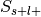
Label-negative and selected –>
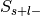
Label-positive and unselected –>
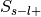
Label-negative and unselected –>
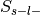
Additionally, the number of foci associated with each of these groups is extracted.
Number of foci from studies with label,
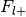
Number of foci from studies without label,
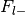
Total number of foci in the database,
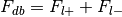
Compute the number of times any label is used in the database,
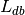 (e.g., if every experiment in the database uses two labels,
then this number is
(e.g., if every experiment in the database uses two labels,
then this number is 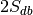 , where
, where 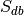 is the total number of experiments in the database).
is the total number of experiments in the database).Compute the probability of being selected,
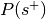 .
.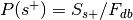 , where
, where 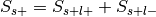
For each label, compute the probability of having the label,
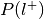 .
.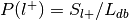 , where
, where 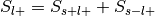
For each label, compute the probability of being selected given presence of the label,
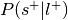 .
.Can be re-interpreted as the probability of activating the ROI given a mental state.
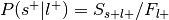
Convert
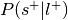 into the forward inference likelihood,
into the forward inference likelihood, 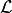 .
.Compute the probability of the label given selection,
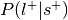 .
.Can be re-interpreted as probability of a mental state given activation of the ROI.
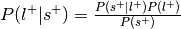
This is the reverse inference posterior probability.
Perform a binomial test to determine if the rate at which studies are selected from the set of studies with the label is significantly different from the base probability of studies being selected across the whole database.
The number of successes is
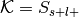 , the number of trials is
, the number of trials is 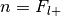 , and the hypothesized probability of success is
, and the hypothesized probability of success is 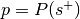
If
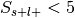 , override the p-value from this test with 1, essentially ignoring this label in the analysis.
, override the p-value from this test with 1, essentially ignoring this label in the analysis.Convert p-value to unsigned z-value.
Perform a two-way chi-square test to determine if presence of the label and selection are independent.
If
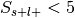 , override the p-value from this test with 1, essentially ignoring this label in the analysis.
, override the p-value from this test with 1, essentially ignoring this label in the analysis.Convert p-value to unsigned z-value.
The Neurosynth approach¶
nimare.decode.discrete.NeurosynthDecoder(), nimare.decode.discrete.neurosynth_decode()
The Neurosynth method for discrete functional decoding performs both forward and reverse inference using an annotated coordinate-based database and a target sample of studies within that database. Unlike the BrainMap approach, the Neurosynth approach uses an a priori value as the prior probability of any given experiment including a given label.
Select studies in the database according to some criterion (e.g., having at least one peak in an ROI).
For each label, studies in the database can now be divided into four groups:
Label-positive and selected –>
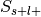
Label-negative and selected –>
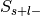
Label-positive and unselected –>
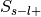
Label-negative and unselected –>
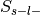
Set a prior probability
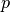 of a given mental state occurring in the real world.
of a given mental state occurring in the real world.Neurosynth uses
0.5as the default.
Compute
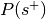 :
:Probability of being selected,
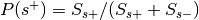 , where
, where 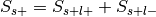 and
and 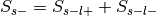
For each label, compute
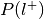 :
: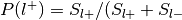 , where
, where 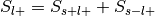 and
and 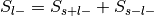
Compute
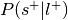 :
:Compute
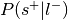 :
: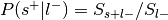
Only used to determine sign of reverse inference z-value.
Compute
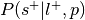 , where is the prior probability of a label:
, where is the prior probability of a label:This is the forward inference posterior probability. Probability of selection given label and given prior probability of label,
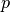 .
.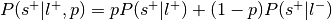
Compute
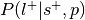 :
:This is the reverse inference posterior probability. Probability of label given selection and given the prior probability of label.
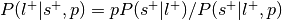
Perform a one-way chi-square test to determine if the rate at which studies are selected for a given label is significantly different from the average rate at which studies are selected across labels.
Convert p-value to signed z-value using whether the number of studies selected for the label is greater than or less than the mean number of studies selected across labels to determine the sign.
Perform a two-way chi-square test to determine if presence of the label and selection are independent.
Convert p-value to signed z-value using
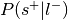 to determine sign.
to determine sign.
The GC-LDA approach¶
nimare.decode.discrete.gclda_decode_roi()
The GC-LDA approach sums 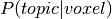 weights within the region of interest to produce topic-wise weights.
weights within the region of interest to produce topic-wise weights.