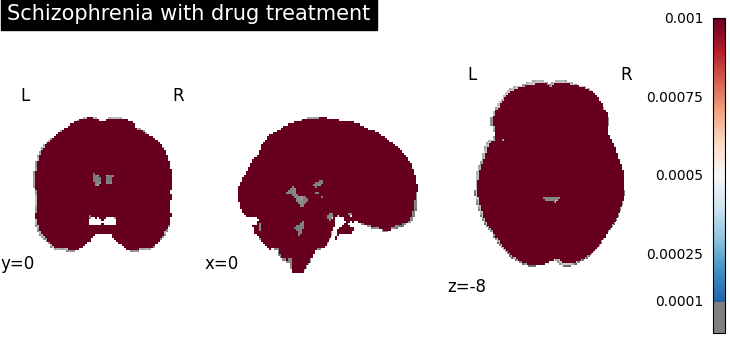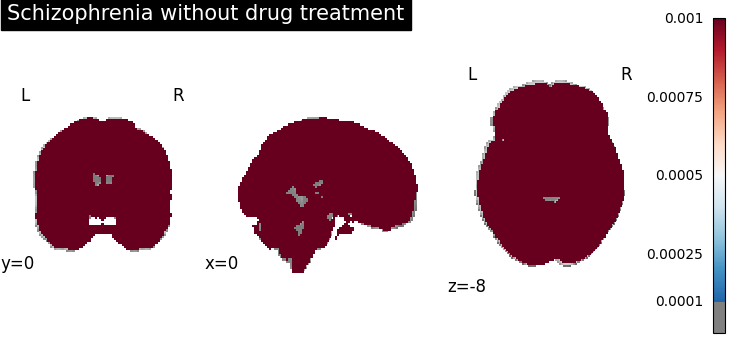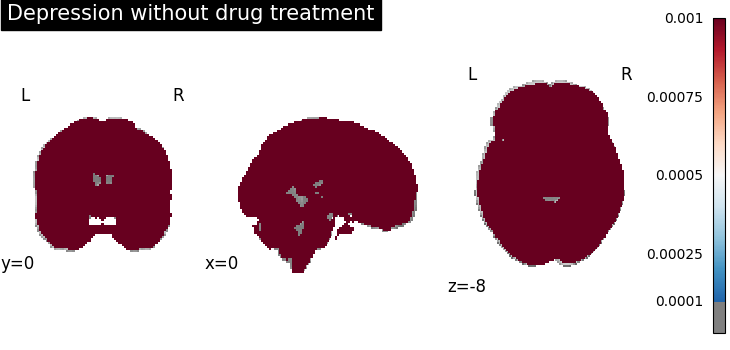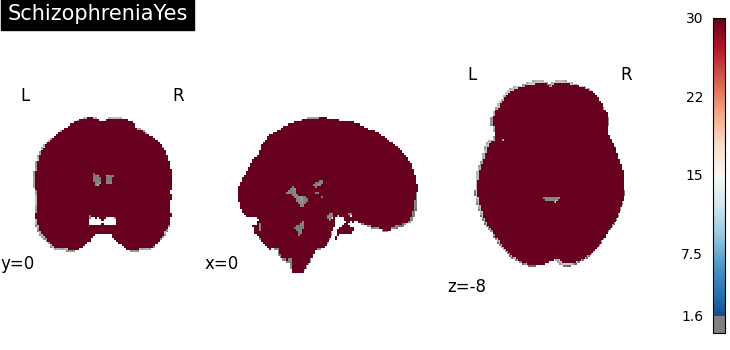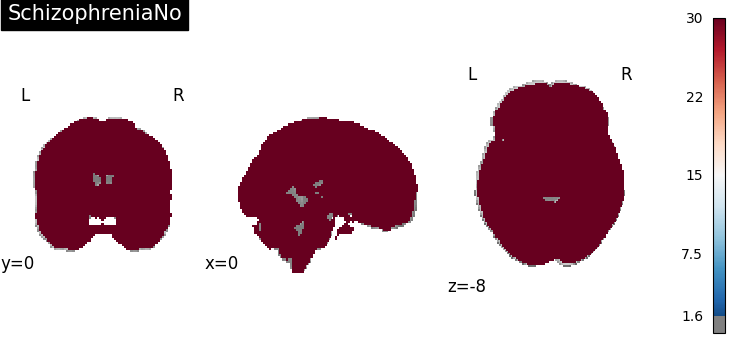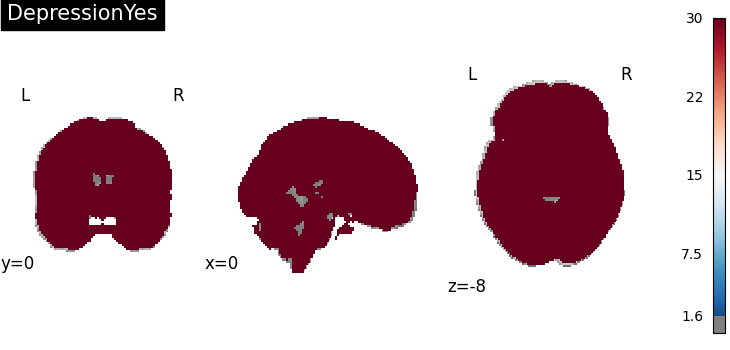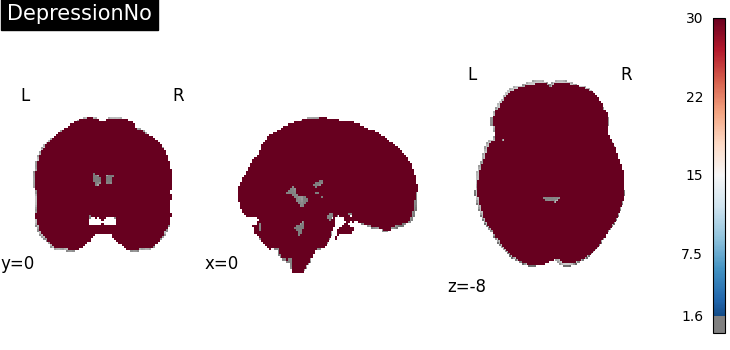Note
Go to the end to download the full example code
Coordinate-based meta-regression algorithms
A tour of Coordinate-based meta-regression (CBMR) algorithms in NiMARE
CBMR is a generative framework to approximate smooth activation intensity function and investigate the effect of study-level moderators (e.g., year of pubilication, sample size, subtype of stimuli). CBMR considers three stochastic models (Poisson, Negative Binomial (NB) and Clustered NB) for modeling the random variation in foci, and allows flexible statistical inference for either spatial homogeneity tests or group comparison tests. It is a computationally efficient approach with good statistical interpretability to model the locations of activation foci.
This tutorial is intended to provide a brief description and example of the CBMR algorithm implemented in NiMARE.
For a more detailed introduction to the elements of a coordinate-based meta-regression, see the online course or a brief overview.
import numpy as np
import scipy
from nilearn.plotting import plot_stat_map
from nimare.generate import create_coordinate_dataset
from nimare.meta import models
from nimare.transforms import StandardizeField
Load Dataset
Here, we’re going to simulate a dataset (using nimare.generate.create_coordinate_dataset that includes 100 studies, each with 10 reported foci and sample size varying between 20 and 40. We separate them into four groups according to diagnosis (schizophrenia or depression) and drug status (Yes or No). We also add two continuous study-level moderators (sample size and average age) and a categorical study-level moderator (schizophrenia subtype).
# data simulation
ground_truth_foci, dset = create_coordinate_dataset(foci=10, sample_size=(20, 40), n_studies=1000)
# set up group columns: diagnosis & drug_status
n_rows = dset.annotations.shape[0]
dset.annotations["diagnosis"] = [
"schizophrenia" if i % 2 == 0 else "depression" for i in range(n_rows)
]
dset.annotations["drug_status"] = ["Yes" if i % 2 == 0 else "No" for i in range(n_rows)]
dset.annotations["drug_status"] = (
dset.annotations["drug_status"].sample(frac=1).reset_index(drop=True)
) # random shuffle drug_status column
# set up continuous moderators: sample sizes & avg_age
dset.annotations["sample_sizes"] = [dset.metadata.sample_sizes[i][0] for i in range(n_rows)]
dset.annotations["avg_age"] = np.arange(n_rows)
# set up categorical moderators: schizophrenia_subtype (as not enough data to be interpreted
# as groups)
dset.annotations["schizophrenia_subtype"] = ["type1", "type2", "type3", "type4", "type5"] * int(
n_rows / 5
)
dset.annotations["schizophrenia_subtype"] = (
dset.annotations["schizophrenia_subtype"].sample(frac=1).reset_index(drop=True)
) # random shuffle drug_status column
Estimation of group-specific spatial intensity functions
CBMR can generate estimation of group-specific spatial internsity functions for multiple groups simultaneously, with different group-specific spatial regression coefficients.
CBMR can also consider the effects of study-level moderators (e.g. sample size, year of publication) by estimating regression coefficients of moderators (shared by all groups).
Note that study-level moderators can only have global effects instead of localized effects within CBMR framework. In the scenario that there’re multiple subgroups within a group (e.g., indexed as subgroup-1 to subgroup-n, but one or more of them don’t have enough number of studies to be inferred as a separate group). Using categorical encoding, CBMR can interpret the subgroups as categorical moderators for each study (either 0 or 1), and estimate the global activation intensity associated with each subgroup (comparing to the average).
from nimare.meta.cbmr import CBMREstimator
dset = StandardizeField(fields=["sample_sizes", "avg_age"]).transform(dset)
cbmr = CBMREstimator(
group_categories=["diagnosis", "drug_status"],
moderators=[
"standardized_sample_sizes",
"standardized_avg_age",
"schizophrenia_subtype:reference=type1",
],
spline_spacing=100, # a reasonable choice is 10 or 5, 100 is for speed
model=models.PoissonEstimator,
penalty=False,
lr=1e-1,
tol=1e3, # a reasonable choice is 1e-2, 1e3 is for speed
device="cpu", # "cuda" if you have GPU
)
results = cbmr.fit(dataset=dset)
Now that we have fitted the model, we can plot the spatial intensity maps.
plot_stat_map(
results.get_map("spatialIntensity_group-SchizophreniaYes"),
cut_coords=[0, 0, -8],
draw_cross=False,
cmap="RdBu_r",
title="Schizophrenia with drug treatment",
threshold=1e-4,
vmax=1e-3,
)
plot_stat_map(
results.get_map("spatialIntensity_group-SchizophreniaNo"),
cut_coords=[0, 0, -8],
draw_cross=False,
cmap="RdBu_r",
title="Schizophrenia without drug treatment",
threshold=1e-4,
vmax=1e-3,
)
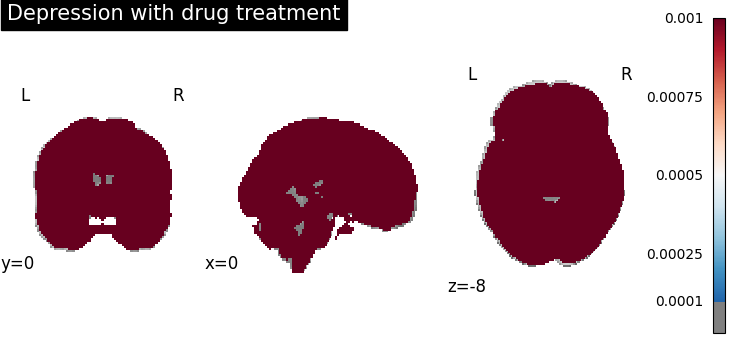
plot_stat_map(
results.get_map("spatialIntensity_group-DepressionYes"),
cut_coords=[0, 0, -8],
draw_cross=False,
cmap="RdBu_r",
title="Depression with drug treatment",
threshold=1e-4,
vmax=1e-3,
)
plot_stat_map(
results.get_map("spatialIntensity_group-DepressionNo"),
cut_coords=[0, 0, -8],
draw_cross=False,
cmap="RdBu_r",
title="Depression without drug treatment",
threshold=1e-4,
vmax=1e-3,
)
<nilearn.plotting.displays._slicers.OrthoSlicer object at 0x7fe9236b9fd0>
Four figures correspond to group-specific spatial intensity map of four groups (“schizophreniaYes”, “schizophreniaNo”, “depressionYes”, “depressionNo”). Areas with stronger spatial intensity are highlighted.
Generalized Linear Hypothesis (GLH) testing for spatial homogeneity
In the most basic scenario of spatial homogeneity test, contrast matrix t_con_groups can be generated by create_contrast function, with group names specified.
from nimare.meta.cbmr import CBMRInference
inference = CBMRInference(device="cuda")
inference.fit(result=results)
t_con_groups = inference.create_contrast(
["SchizophreniaYes", "SchizophreniaNo", "DepressionYes", "DepressionNo"], source="groups"
)
contrast_result = inference.transform(t_con_groups=t_con_groups)
Now that we have done spatial homogeneity tests, we can plot the z-score maps.
# generate z-score maps for group-wise spatial homogeneity test
plot_stat_map(
contrast_result.get_map("z_group-SchizophreniaYes"),
cut_coords=[0, 0, -8],
draw_cross=False,
cmap="RdBu_r",
title="SchizophreniaYes",
threshold=scipy.stats.norm.isf(0.05),
vmax=30,
)
plot_stat_map(
contrast_result.get_map("z_group-SchizophreniaNo"),
cut_coords=[0, 0, -8],
draw_cross=False,
cmap="RdBu_r",
title="SchizophreniaNo",
threshold=scipy.stats.norm.isf(0.05),
vmax=30,
)
plot_stat_map(
contrast_result.get_map("z_group-DepressionYes"),
cut_coords=[0, 0, -8],
draw_cross=False,
cmap="RdBu_r",
title="DepressionYes",
threshold=scipy.stats.norm.isf(0.05),
vmax=30,
)
plot_stat_map(
contrast_result.get_map("z_group-DepressionNo"),
cut_coords=[0, 0, -8],
draw_cross=False,
cmap="RdBu_r",
title="DepressionNo",
threshold=scipy.stats.norm.isf(0.05),
vmax=30,
)
<nilearn.plotting.displays._slicers.OrthoSlicer object at 0x7fe923f39520>
Four figures (displayed as z-statistics map) correspond to homogeneity test of
group-specific spatial intensity for four groups. The null hypothesis assumes
homogeneous spatial intensity over the whole brain,
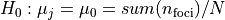 ,
, 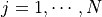 , where
, where
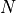 is the number of voxels within brain mask,
is the number of voxels within brain mask, 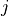 is the index of voxel.
Areas with significant p-values are highlighted (under significance level
is the index of voxel.
Areas with significant p-values are highlighted (under significance level 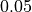 ).
).
Perform fasle discovery rate (FDR) correction on spatial homogeneity test
The default FDR correction method is “indep”, using Benjamini-Hochberg(BH) procedure.
from nimare.correct import FDRCorrector
corr = FDRCorrector(method="indep", alpha=0.05)
cres = corr.transform(contrast_result)
Now that we have applied the FDR correction methods, we can plot the FDR corrected z-score maps.
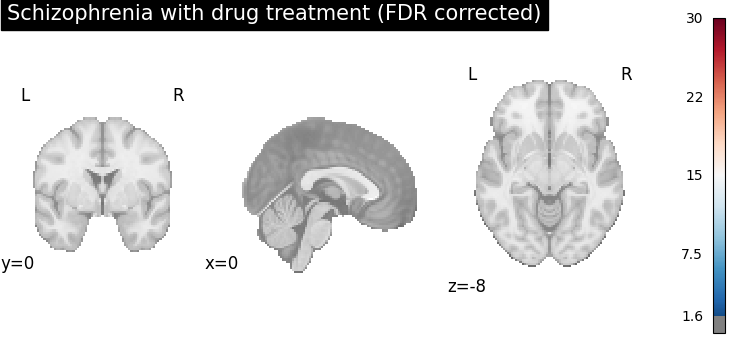
# generate FDR corrected z-score maps for group-wise spatial homogeneity test
plot_stat_map(
cres.get_map("z_group-SchizophreniaYes_corr-FDR_method-indep"),
cut_coords=[0, 0, -8],
draw_cross=False,
cmap="RdBu_r",
title="Schizophrenia with drug treatment (FDR corrected)",
threshold=scipy.stats.norm.isf(0.05),
vmax=30,
)
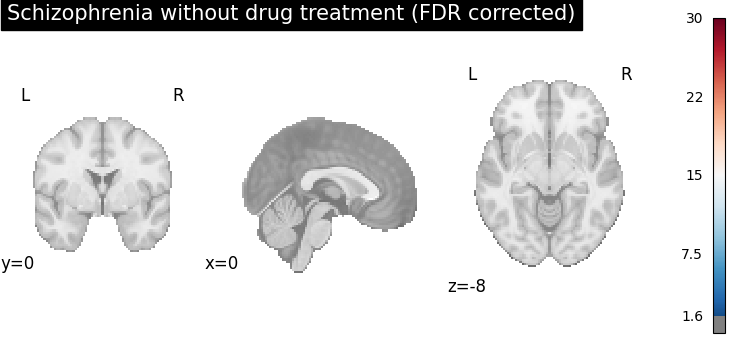
plot_stat_map(
cres.get_map("z_group-SchizophreniaNo_corr-FDR_method-indep"),
cut_coords=[0, 0, -8],
draw_cross=False,
cmap="RdBu_r",
title="Schizophrenia without drug treatment (FDR corrected)",
threshold=scipy.stats.norm.isf(0.05),
vmax=30,
)
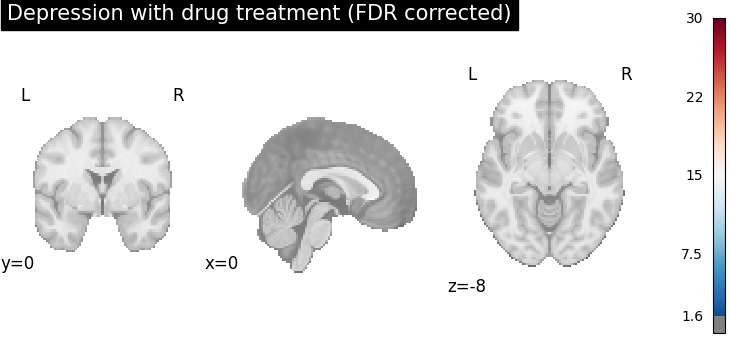
plot_stat_map(
cres.get_map("z_group-DepressionYes_corr-FDR_method-indep"),
cut_coords=[0, 0, -8],
draw_cross=False,
cmap="RdBu_r",
title="Depression with drug treatment (FDR corrected)",
threshold=scipy.stats.norm.isf(0.05),
vmax=30,
)
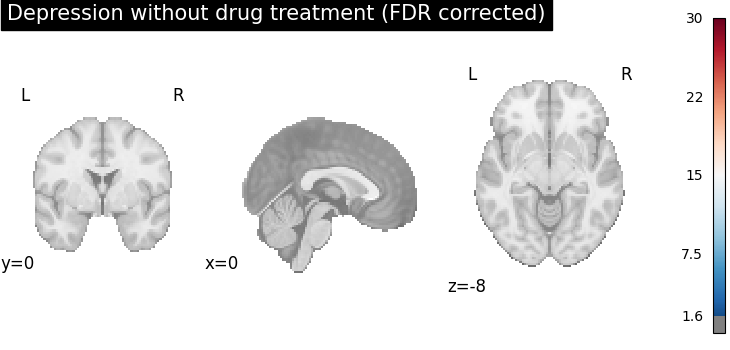
plot_stat_map(
cres.get_map("z_group-DepressionNo_corr-FDR_method-indep"),
cut_coords=[0, 0, -8],
draw_cross=False,
cmap="RdBu_r",
title="Depression without drug treatment (FDR corrected)",
threshold=scipy.stats.norm.isf(0.05),
vmax=30,
)
/home/docs/checkouts/readthedocs.org/user_builds/nimare/envs/latest/lib/python3.9/site-packages/nilearn/_utils/niimg.py:61: UserWarning:
Non-finite values detected. These values will be replaced with zeros.
/home/docs/checkouts/readthedocs.org/user_builds/nimare/envs/latest/lib/python3.9/site-packages/nilearn/plotting/displays/_slicers.py:438: UserWarning:
empty mask
<nilearn.plotting.displays._slicers.OrthoSlicer object at 0x7fe923835070>
After FDR correction (via BH procedure), areas with stronger spatial intensity are more stringent, (the number of voxels with significant p-values is reduced).
GLH testing for group comparisons among any two groups
In the most basic scenario of group comparison test, contrast matrix t_con_groups can be generated by create_contrast function, with contrast_name specified as “group1-group2”.
t_con_groups = inference.create_contrast(
[
"SchizophreniaYes-SchizophreniaNo",
"SchizophreniaNo-DepressionNo",
"DepressionYes-DepressionNo",
],
source="groups",
)
contrast_result = inference.transform(t_con_groups=t_con_groups, t_con_moderators=False)
Now that we have done group comparison tests, we can plot the z-score maps indicating difference in spatial intensity between two groups.
# generate z-statistics maps for each group
plot_stat_map(
contrast_result.get_map("z_group-SchizophreniaYes-SchizophreniaNo"),
cut_coords=[0, 0, -8],
draw_cross=False,
cmap="RdBu_r",
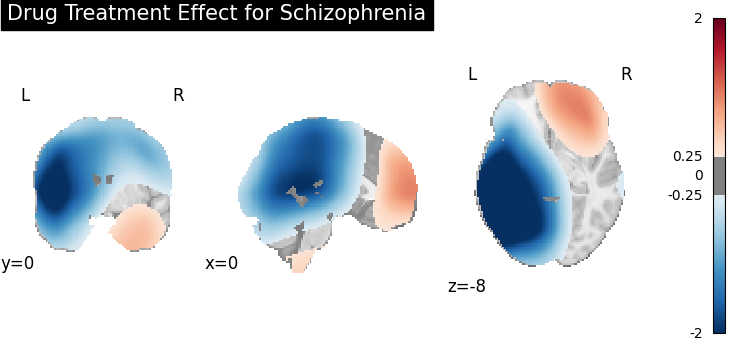
title="Drug Treatment Effect for Schizophrenia",
threshold=scipy.stats.norm.isf(0.4),
vmax=2,
)
plot_stat_map(
contrast_result.get_map("z_group-SchizophreniaNo-DepressionNo"),
cut_coords=[0, 0, -8],
draw_cross=False,
cmap="RdBu_r",
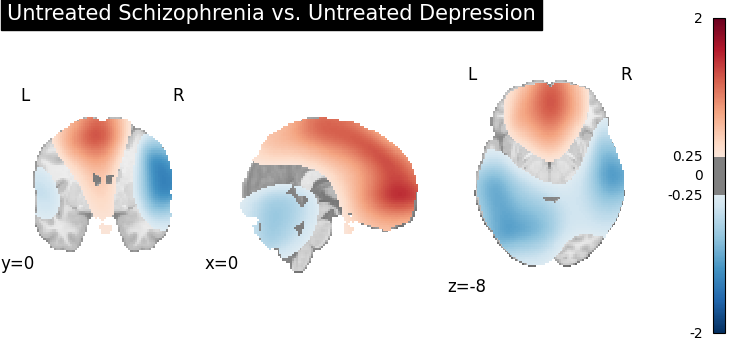
title="Untreated Schizophrenia vs. Untreated Depression",
threshold=scipy.stats.norm.isf(0.4),
vmax=2,
)
plot_stat_map(
contrast_result.get_map("z_group-DepressionYes-DepressionNo"),
cut_coords=[0, 0, -8],
draw_cross=False,
cmap="RdBu_r",
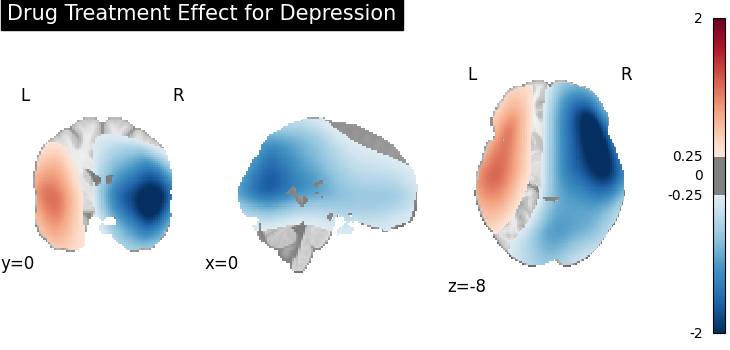
title="Drug Treatment Effect for Depression",
threshold=scipy.stats.norm.isf(0.4),
vmax=2,
)
<nilearn.plotting.displays._slicers.OrthoSlicer object at 0x7fe9191affd0>
Four figures (displayed as z-statistics map) correspond to group comparison
test of spatial intensity for any two groups. The null hypothesis assumes
spatial intensity estimations of two groups are equal at voxel level,
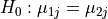 ,
, 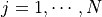 , where
, where 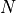 is number
of voxels within brain mask,
is number
of voxels within brain mask, 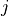 is the index of voxel. Areas with significant p-values
(significant difference in spatial intensity estimation between two groups)
are highlighted (under significance level
is the index of voxel. Areas with significant p-values
(significant difference in spatial intensity estimation between two groups)
are highlighted (under significance level 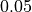 ).
).
GLH testing with contrast matrix specified
CBMR supports more flexible GLH test by specifying a contrast matrix. For example, group comparison test 2xgroup_0-1xgroup_1-1xgroup_2 can be represented as t_con_group=[2, -1, -1, 0], as an input in compute_contrast function. Multiple independent GLH tests can be conducted simultaneously by including multiple contrast vectors/matrices in t_con_group.
CBMR also allows simultaneous GLH tests (consisting of multiple contrast vectors)
when it’s represented as one of elements in t_con_group (datatype: list).
Only if all of null hypotheses are rejected at voxel level, p-values are significant.
For example, t_con_group=[[1,-1,0,0], [1,0,-1,0], [0,0,1,-1]] is used for testing
the equality of spatial intensity estimation among all of four groups (finding the
consistent activation regions). Note that only 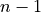 contrast vectors are necessary
for testing the equality of
contrast vectors are necessary
for testing the equality of 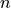 groups.
groups.
contrast_result = inference.transform(
t_con_groups=[[[1, -1, 0, 0], [1, 0, -1, 0], [0, 0, 1, -1]]], t_con_moderators=False
)
Now that we have done group comparison tests with the specified contrast matrix, we can plot the z-score maps indicating uniformity in activation regions among all four groups.
plot_stat_map(
contrast_result.get_map("z_GLH_groups_0"),
cut_coords=[0, 0, -8],
draw_cross=False,
cmap="RdBu_r",
title="GLH_groups_0",
threshold=scipy.stats.norm.isf(0.4),
)
print("The contrast matrix of GLH_0 is {}".format(contrast_result.metadata["GLH_groups_0"]))
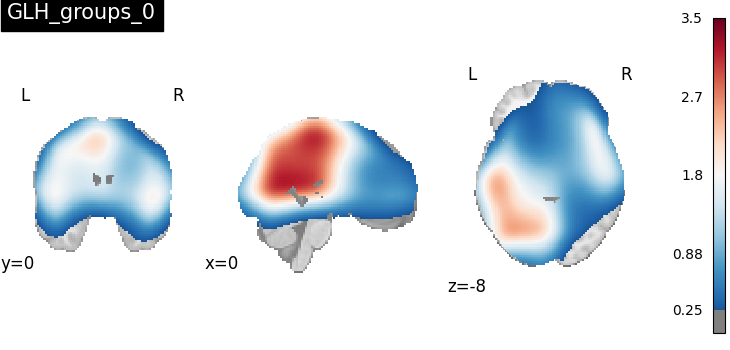
The contrast matrix of GLH_0 is [[1, -1, 0, 0], [1, 0, -1, 0], [0, 0, 1, -1]]
GLH testing for study-level moderators
CBMR framework can estimate global study-level moderator effects, and allows inference on the existence of m.
contrast_name = results.estimator.moderators
t_con_moderators = inference.create_contrast(contrast_name, source="moderators")
contrast_result = inference.transform(t_con_moderators=t_con_moderators)
print(contrast_result.tables["moderators_regression_coef"])
print(
"P-values of moderator effects `sample_sizes` is {}".format(
contrast_result.tables["p_standardized_sample_sizes"]
)
)
print(
"P-value of moderator effects `avg_age` is {}".format(
contrast_result.tables["p_standardized_avg_age"]
)
)
standardized_sample_sizes standardized_avg_age ... type4 type5
0 0.000455 -0.00647 ... -0.460327 -0.462119
[1 rows x 6 columns]
P-values of moderator effects `sample_sizes` is p
0 8.899303e-09
P-value of moderator effects `avg_age` is p
0 0.0
This table shows the regression coefficients of study-level moderators, here,
sample_sizes and avg_age are standardized in the preprocessing steps.
Moderator effects of both sample_size and avg_age are not significant under
significance level 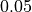 . With reference to spatial intensity estimation of
a chosen subtype, spatial intensity estimations of the other
. With reference to spatial intensity estimation of
a chosen subtype, spatial intensity estimations of the other 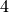 subtypes of
schizophrenia are moderatored globally.
subtypes of
schizophrenia are moderatored globally.
t_con_moderators = inference.create_contrast(
["standardized_sample_sizes-standardized_avg_age"], source="moderators"
)
contrast_result = inference.transform(t_con_moderators=t_con_moderators)
print(
"P-values of difference in two moderator effectors (`sample_size-avg_age`) is {}".format(
contrast_result.tables["p_standardized_sample_sizes-standardized_avg_age"]
)
)
P-values of difference in two moderator effectors (`sample_size-avg_age`) is p
0 0.0
CBMR also allows flexible contrasts between study-level covariates. For example, we can write contrast_name (an input to create_contrast function) as standardized_sample_sizes-standardized_avg_age when exploring if the moderator effects of sample_sizes and avg_age are equivalent.
Total running time of the script: (2 minutes 32.546 seconds)