Note
Go to the end to download the full example code
The Cognitive Atlas
Download the Cognitive Atlas and extract CogAt terms from text.
import os
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from nimare import annotate, extract
from nimare.dataset import Dataset
from nimare.utils import get_resource_path
Load dataset with abstracts
dset = Dataset(os.path.join(get_resource_path(), "neurosynth_laird_studies.json"))
Download Cognitive Atlas
cogatlas = extract.download_cognitive_atlas(data_dir=get_resource_path(), overwrite=False)
id_df = pd.read_csv(cogatlas["ids"])
rel_df = pd.read_csv(cogatlas["relationships"])
ID DataFrame
Relationships DataFrame
Extract Cognitive Atlas terms from text
counts_df, rep_text_df = annotate.cogat.extract_cogat(dset.texts, id_df, text_column="abstract")
Expand counts
weights = {"isKindOf": 1, "isPartOf": 1, "inCategory": 1}
expanded_df = annotate.cogat.expand_counts(counts_df, rel_df, weights)
# Sort by total count and reduce for better visualization
series = expanded_df.sum(axis=0)
series = series.sort_values(ascending=False)
series = series[series > 0]
columns = series.index.tolist()
/home/docs/checkouts/readthedocs.org/user_builds/nimare/checkouts/stable/nimare/annotate/utils.py:45: FutureWarning:
The provided callable <function max at 0x7ffb261ccc10> is currently using DataFrameGroupBy.max. In a future version of pandas, the provided callable will be used directly. To keep current behavior pass the string "max" instead.
/home/docs/checkouts/readthedocs.org/user_builds/nimare/checkouts/stable/nimare/annotate/cogat.py:204: PerformanceWarning:
DataFrame is highly fragmented. This is usually the result of calling `frame.insert` many times, which has poor performance. Consider joining all columns at once using pd.concat(axis=1) instead. To get a de-fragmented frame, use `newframe = frame.copy()`
/home/docs/checkouts/readthedocs.org/user_builds/nimare/checkouts/stable/nimare/annotate/cogat.py:204: PerformanceWarning:
DataFrame is highly fragmented. This is usually the result of calling `frame.insert` many times, which has poor performance. Consider joining all columns at once using pd.concat(axis=1) instead. To get a de-fragmented frame, use `newframe = frame.copy()`
/home/docs/checkouts/readthedocs.org/user_builds/nimare/checkouts/stable/nimare/annotate/cogat.py:204: PerformanceWarning:
DataFrame is highly fragmented. This is usually the result of calling `frame.insert` many times, which has poor performance. Consider joining all columns at once using pd.concat(axis=1) instead. To get a de-fragmented frame, use `newframe = frame.copy()`
/home/docs/checkouts/readthedocs.org/user_builds/nimare/checkouts/stable/nimare/annotate/cogat.py:204: PerformanceWarning:
DataFrame is highly fragmented. This is usually the result of calling `frame.insert` many times, which has poor performance. Consider joining all columns at once using pd.concat(axis=1) instead. To get a de-fragmented frame, use `newframe = frame.copy()`
/home/docs/checkouts/readthedocs.org/user_builds/nimare/checkouts/stable/nimare/annotate/cogat.py:204: PerformanceWarning:
DataFrame is highly fragmented. This is usually the result of calling `frame.insert` many times, which has poor performance. Consider joining all columns at once using pd.concat(axis=1) instead. To get a de-fragmented frame, use `newframe = frame.copy()`
/home/docs/checkouts/readthedocs.org/user_builds/nimare/checkouts/stable/nimare/annotate/cogat.py:204: PerformanceWarning:
DataFrame is highly fragmented. This is usually the result of calling `frame.insert` many times, which has poor performance. Consider joining all columns at once using pd.concat(axis=1) instead. To get a de-fragmented frame, use `newframe = frame.copy()`
/home/docs/checkouts/readthedocs.org/user_builds/nimare/checkouts/stable/nimare/annotate/cogat.py:204: PerformanceWarning:
DataFrame is highly fragmented. This is usually the result of calling `frame.insert` many times, which has poor performance. Consider joining all columns at once using pd.concat(axis=1) instead. To get a de-fragmented frame, use `newframe = frame.copy()`
/home/docs/checkouts/readthedocs.org/user_builds/nimare/checkouts/stable/nimare/annotate/cogat.py:204: PerformanceWarning:
DataFrame is highly fragmented. This is usually the result of calling `frame.insert` many times, which has poor performance. Consider joining all columns at once using pd.concat(axis=1) instead. To get a de-fragmented frame, use `newframe = frame.copy()`
/home/docs/checkouts/readthedocs.org/user_builds/nimare/checkouts/stable/nimare/annotate/cogat.py:204: PerformanceWarning:
DataFrame is highly fragmented. This is usually the result of calling `frame.insert` many times, which has poor performance. Consider joining all columns at once using pd.concat(axis=1) instead. To get a de-fragmented frame, use `newframe = frame.copy()`
/home/docs/checkouts/readthedocs.org/user_builds/nimare/checkouts/stable/nimare/annotate/cogat.py:204: PerformanceWarning:
DataFrame is highly fragmented. This is usually the result of calling `frame.insert` many times, which has poor performance. Consider joining all columns at once using pd.concat(axis=1) instead. To get a de-fragmented frame, use `newframe = frame.copy()`
/home/docs/checkouts/readthedocs.org/user_builds/nimare/checkouts/stable/nimare/annotate/cogat.py:204: PerformanceWarning:
DataFrame is highly fragmented. This is usually the result of calling `frame.insert` many times, which has poor performance. Consider joining all columns at once using pd.concat(axis=1) instead. To get a de-fragmented frame, use `newframe = frame.copy()`
Make some plots
We will reduce the dataframes to only columns with at least one count to make visualization easier.
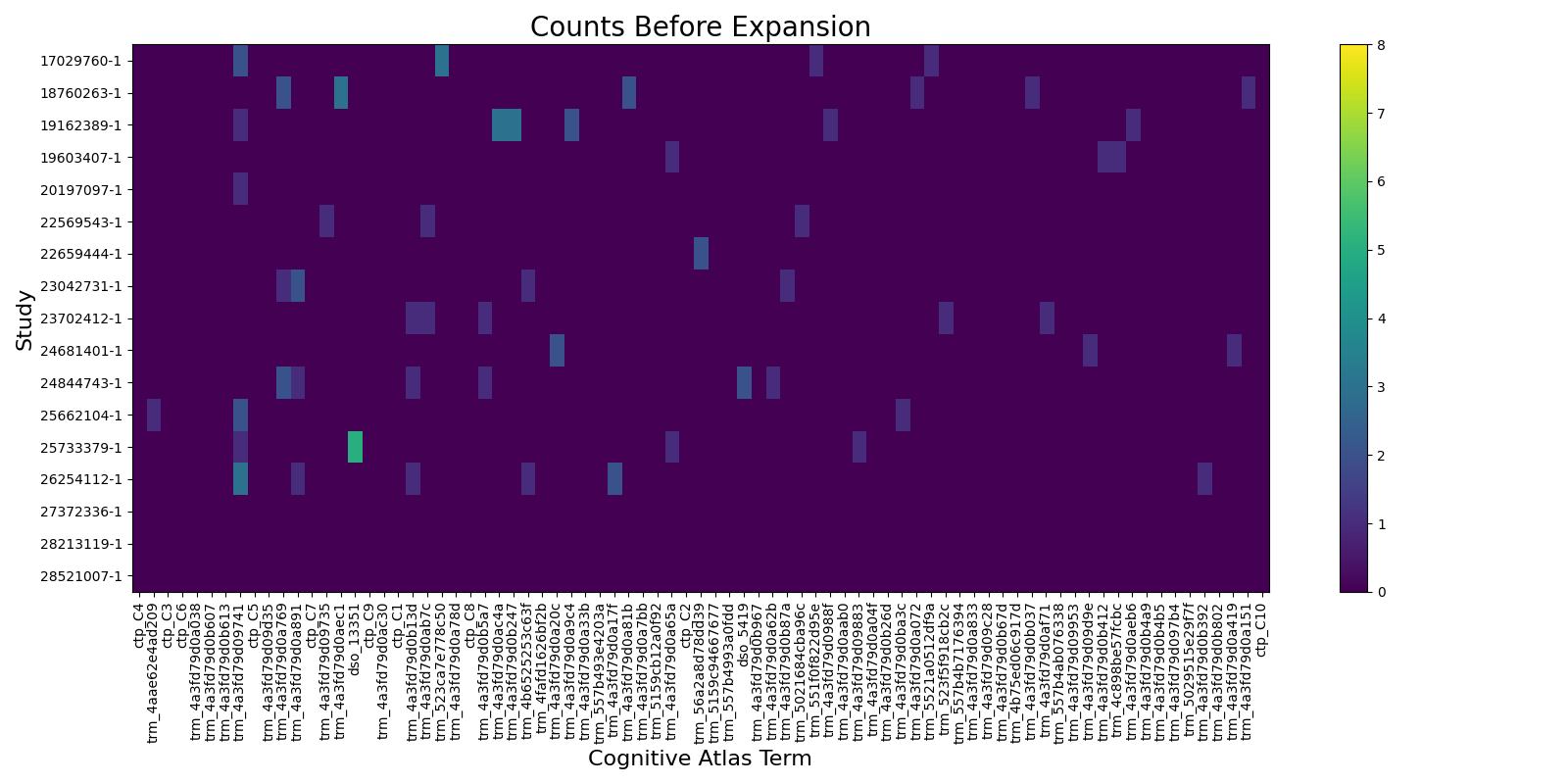
# Raw counts
fig1, ax1 = plt.subplots(figsize=(16, 8))
pos = ax1.imshow(counts_df[columns].values, aspect="auto", vmin=0, vmax=np.max(expanded_df.values))
fig1.colorbar(pos, ax=ax1)
ax1.set_title("Counts Before Expansion", fontsize=20)
ax1.set_yticks(range(counts_df.shape[0]))
ax1.set_yticklabels(counts_df.index)
ax1.set_ylabel("Study", fontsize=16)
ax1.set_xticks(range(len(columns)))
ax1.set_xticklabels(columns, rotation=90)
ax1.set_xlabel("Cognitive Atlas Term", fontsize=16)
fig1.tight_layout()
fig1.show()
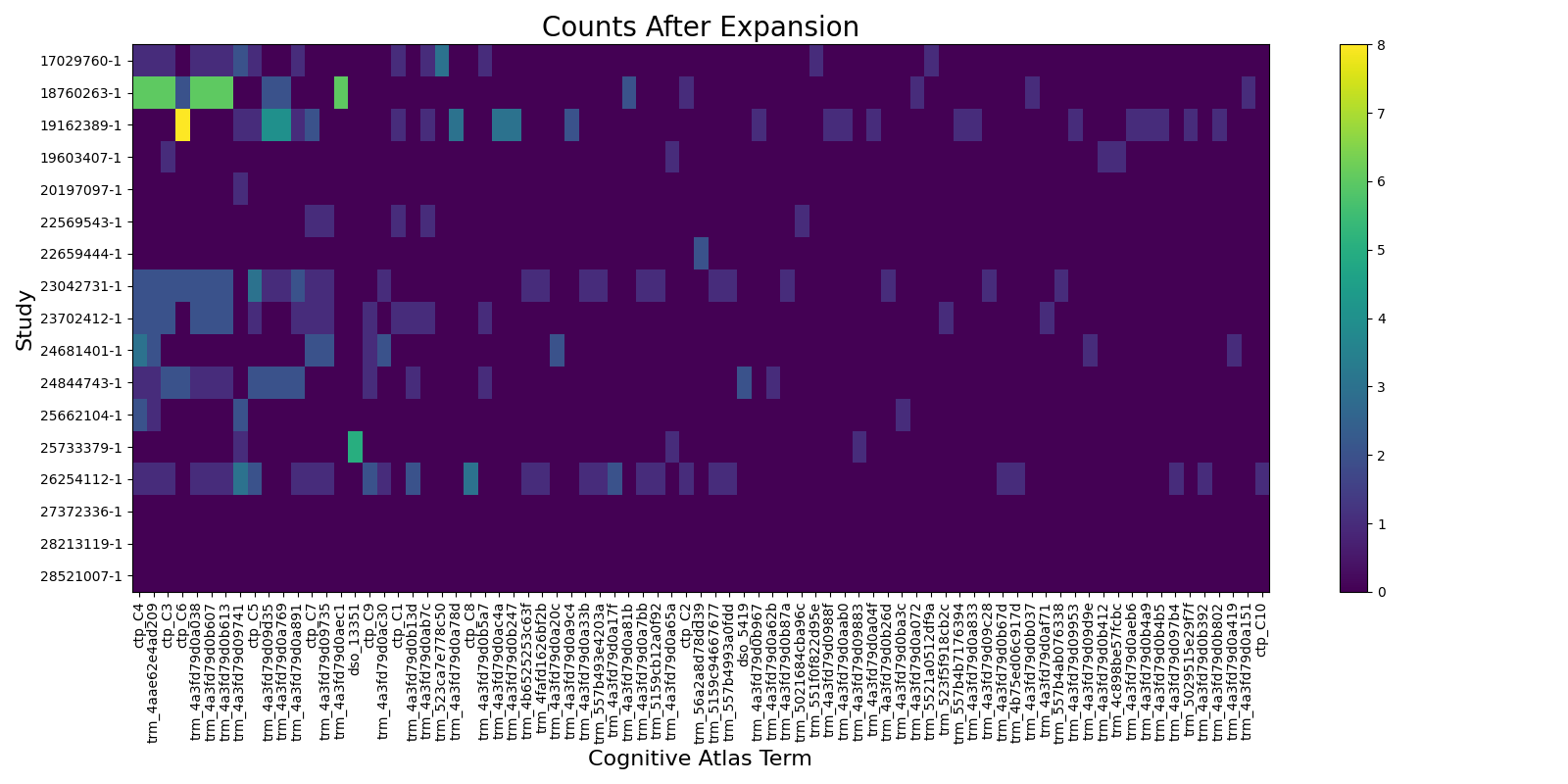
# Expanded counts
fig2, ax2 = plt.subplots(figsize=(16, 8))
pos = ax2.imshow(
expanded_df[columns].values, aspect="auto", vmin=0, vmax=np.max(expanded_df.values)
)
fig2.colorbar(pos, ax=ax2)
ax2.set_title("Counts After Expansion", fontsize=20)
ax2.set_yticks(range(counts_df.shape[0]))
ax2.set_yticklabels(counts_df.index)
ax2.set_ylabel("Study", fontsize=16)
ax2.set_xticks(range(len(columns)))
ax2.set_xticklabels(columns, rotation=90)
ax2.set_xlabel("Cognitive Atlas Term", fontsize=16)
fig2.tight_layout()
fig2.show()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 11.640 seconds)